05/10/2021. Scientists from the Medical Informatics Initiative (MII) presented various IT applications for data sharing, processing and analysis in an MII session at the GMDS-TMF Annual Digital Congress 2021 on 29 September 2021. These were developed by the MII consortia and help to ensure that healthcare data can be used for medical research in order to improve prevention and treatment options for patients.
Magdalena Smieszek from the Klaus Tschira Institute for Computer Cardiology at Heidelberg University Hospital, presented for instance a web application that clinicians can use in order to evaluate medical data from patients with heart failure more quickly.
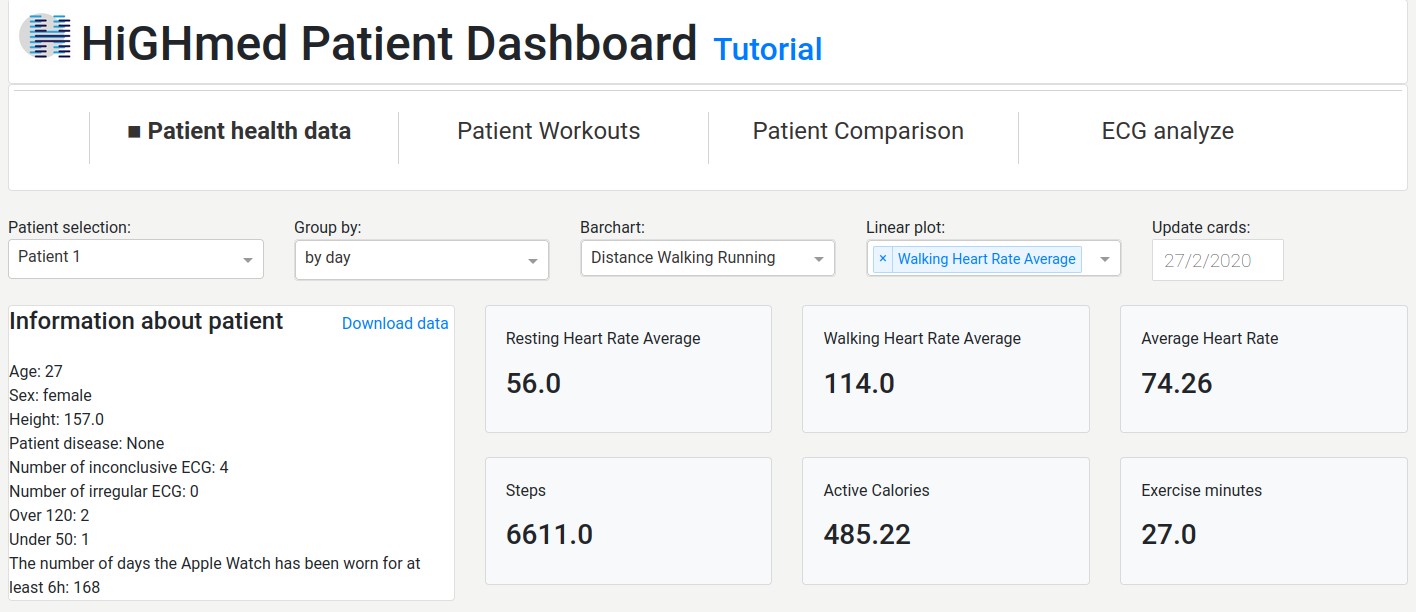
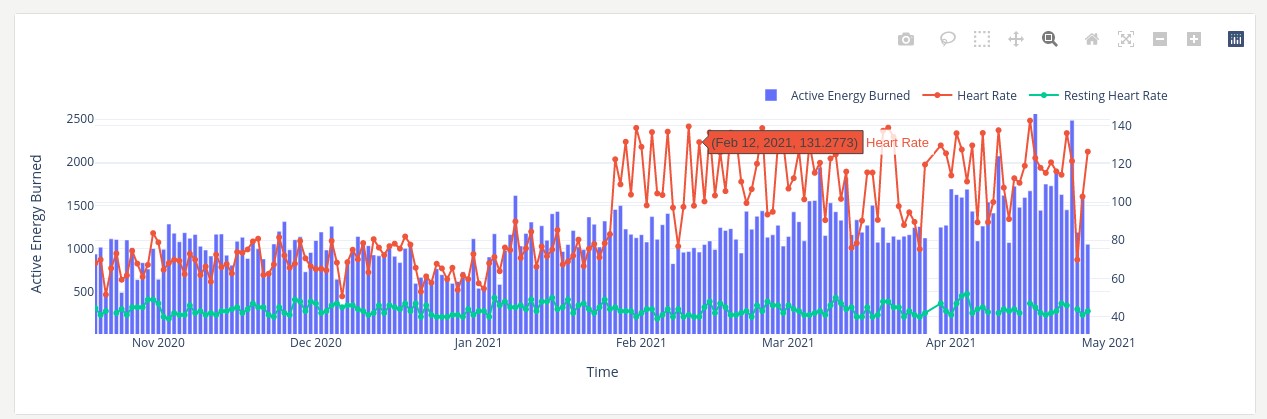
As part of the cardiology use case of the HiGHmed consortium of the MII, a dashboard was developed that enables a visualization and analysis of data collected via Apple Watch. In the cardiology use case, patients are equipped with wearable sensors and apps to record activity parameters and heart rate data outside of the university hospital. In the long term, the analysis of this data should make it possible to detect deterioration episodes in patients with a high risk of severe disease progression at an early stage, to improve their quality of life and to reduce hospital stays.
With the dashboard, doctors can analyse the data collected with the smartwatch more quickly and recognise changes as well as draw conclusions from patients' behavioural patterns to their state of health. The visual representation of the data also facilitates interpretation.
The web application is an open source solution and is available to clinicians and researchers:
Reto Wettstein from the Institute of Medical Informatics at the Heidelberg University Hospital demonstrated in his talk how the process of data sharing for secondary use is implemented in the HiGHmed consortium. The automated process enables data sharing across several institutions, using the BPMN2.0 and HL7 FHIR R4 standards. Thereby, identifying patient data does not leave the respective institution and pseudonymised medical data is only made available for approved research projects. For this purpose, technologies such as a record linkage algorithm based on bloom filters and a two-step pseudonymisation concept are applied. With this process, data from different institutions can be extracted from primary systems, merged, pseudonymised and made available in a data protection-compliant manner.
In the HiGHmed consortium, these IT solutions are currently being implemented at eight university hospitals and one Trusted Third Party. The generic approach of the process using open standards and an open-source reference implementation allows other MII sites to use it as well.